|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
 |
The TCP/IP Guide 9 Networking Fundamentals 9 Backgrounder: Data Representation and the Mathematics of Computing |
|
Decimal, Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal Numbers
(Page 2 of 3)
Making Binary Numbers Easier to Use By Grouping Bits
One problem with binary numbers is that while computers love them, they are unintuitive for humans, who are used to decimal numbers. One reason for this is that they quickly get very, very long and cumbersome to deal with. For example, 1,000,000 in decimal is 11110100001001000000 in binary. To make binary numbers easier to work with, two different shorthand notations have been defined. In both of these, instead of working with each bit individually, they are collected into subgroups, each of which is assigned a single digit in an alternative numbering system.
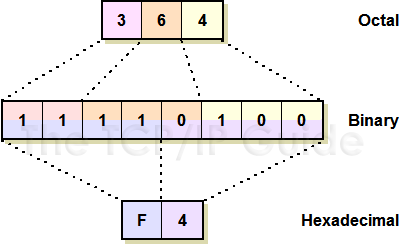
Let's take the binary number 11110100, which is 244 in decimal. Now, instead of looking at each bit individually, let's chop them into groups of three, starting from the right. So, 11110100 becomes (11)(110)(100). Now, each of those groups has three bits, so each can have 23 values: from 0 to 7. In this case, (11)(110)(100) = (3)(6)(4), or 364 in the octal or base-8 numbering system (see Figure 9). Just as with binary, octal numbers are the same as decimal numbers, except they are base 8 instead of base 10. So, 364 in octal is just 3 times 64 plus 6 times 8 plus 4, or 244. The advantage that octal has over binary is obvious: it's a lot less cumbersome to deal with larger numbers. 1,000,000 in decimal is 3641100 in octal.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.