 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
NNTP Client-Server Communication Process: News Posting and Access
(Page 3 of 4)
News Access Methods
There are several different ways that the newsreader can access messages in a group, depending on how it is programmed and on what the user of the software wants.
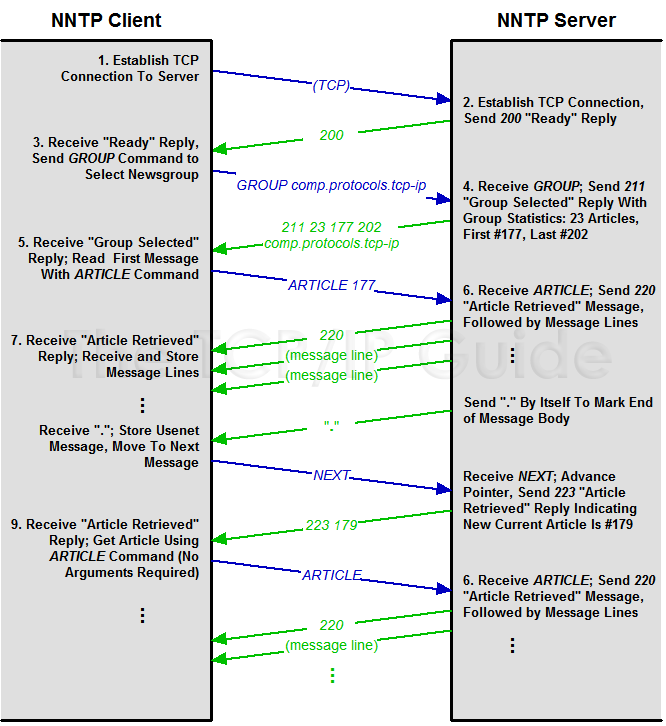
This is the “brute force” technique: the client simply requests that the server send it all the messages in the group. This is done by issuing the ARTICLE command to select the first current message in the group, using the first article number returned by the GROUP command. This sets the server's internal pointer for the session to point to the first article, so it can be retrieved. The NEXT command is then used to advance the pointer to the next message, and the ARTICLE command to retrieve it. This continues until the entire group has been read. Figure 313 illustrates the process.
|
The retrieved messages are stored by the newsreader and available for instant access by the user. This method is most suitable for relatively small newsgroups and/or users with fast Internet connections.
Since downloading an entire newsgroup is time-consuming, many newsreaders compromise by downloading the headers of all messages instead of the full message. The process is the same as for full newsgroup retrieval, but the HEAD command is used to retrieve just an article's headers instead of the ARTICLE command. This takes less time than retrieving each message in its entirety.
The XHDR command extension can also be used, if the server supports it, to more efficiently retrieve only a subset of the headers for the messages, such as the subject line and author.
It is also possible to retrieve a single message from a group, using the ARTICLE command and specifying the article's message identifier.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: While NNTP is best known for its role in inter-server propagation, it is also used by Usenet clients to write and read articles. A number of different commands provides flexibility in how articles can be read by a client device. A client can retrieve an entire newsgroup, only a set of newsgroup headers, or individual articles. Other commands also support various administrative functions.
Key Concept: While NNTP is best known for its role in inter-server propagation, it is also used by Usenet clients to write and read articles. A number of different commands provides flexibility in how articles can be read by a client device. A client can retrieve an entire newsgroup, only a set of newsgroup headers, or individual articles. Other commands also support various administrative functions.