|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
PPP Link Setup and Phases
(Page 1 of 3)
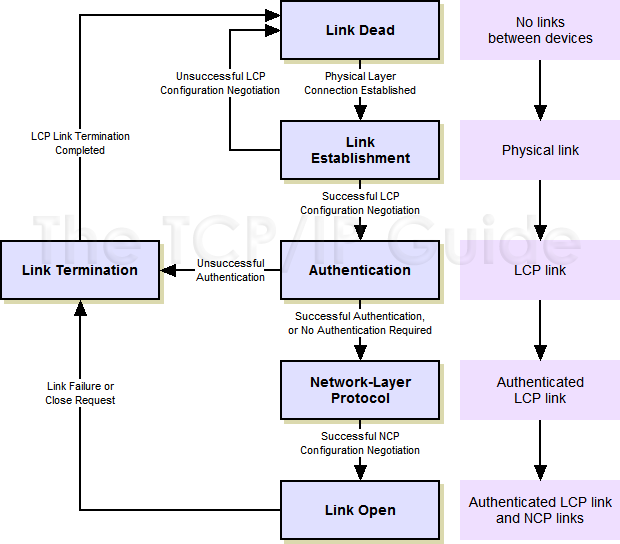
Before data can be exchanged on a PPP connection, a link must be set up between the two devices. As part of this setup task, a configuration process is undertaken whereby the two configure the link and agree on the parameters for how data should be passed between them. Only after this is completed can frames actually pass over the link.
The PPP Link Configuration Protocol (LCP) is generally in charge of setting up and maintaining PPP links. LCP may invoke an authentication protocol (PAP or CHAP) when PPP is configured to use authentication. After an LCP link has been opened, PPP invokes one or more Network Control Protocols (NCPs) for the layer three protocol being carried on the link. These perform any network-layer-specific configuration needed before the link can carry that particular network layer protocol.
The operation of a PPP link can be described as having a “life” of sort. Just as humans are born, grow, have an adult life span and then die, a PPP link is established, configured, used and eventually terminated. The process of setting up, using and closing a PPP link is described in the PPP standard as a series of phases or states. This is a type of finite state machine (FSM), a tool used to explain the operation of protocols.
|
When we talk about a PPP link overall, we are talking about the status of the LCP connection between the two devices; again, LCP governs the overall state of PPP as a whole. Once an LCP link has been opened, each of the NCPs used on the link can be opened or closed independently of the overall PPP (LCP) link. We'll see how this works momentarily.
An excellent way of understanding how PPP works is to look at these phases, and the process by which transition is made from one to the next during the lifetime of the link. For purposes of clarity, this description is based on an example where device A is a PC performing a dial-up networking connection to a remote host B (see Figure 25).
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Background Information: The general concept behind an FSM is described in
Background Information: The general concept behind an FSM is described in