|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
PPP Overview, History and Benefits
(Page 2 of 3)
PPP General Function and Architecture
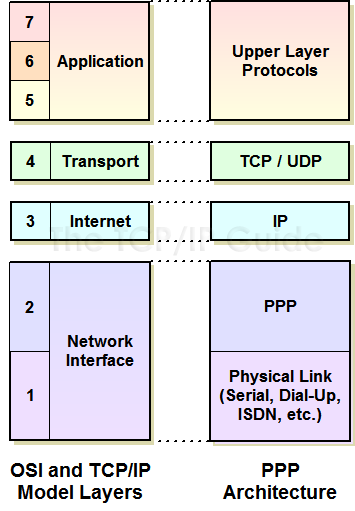
PPP is a connection-oriented protocol that enables layer two links over a variety of different physical layer connections. It is supported on both synchronous and asynchronous lines, and can operate in half-duplex or full-duplex mode. It was designed to carry IP traffic but is general enough to allow any type of network layer datagram to be sent over a PPP connection. As its name implies, it is for point-to-point connections between exactly two devices, and assumes that frames are sent and received in the same order.
PPP fits into the Network Interface layer (Link Layer) in the TCP/IP model, as shown in Figure 23. The operation of PPP follows a specific sequence described in the general operation topic, including a multi-step link establishment phase that may include optional authentication.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.