 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
SNMP Protocol Object Modification Using SetRequest Messages
The GetRequest-PDU, GetNextRequest-PDU, and GetBulkRequest-PDU messages are the three members of the SNMP “Read” class of PDUs—they are used to let an SNMP manager read MIB objects from an MIB agent. The opposite function is represented by the SNMP “Write” class, which contains a single member: the SNMP SetRequest-PDU message.
The use of this PDU is fairly obvious; where one of the three Get PDUs specifies a variable whose value is to be retrieved, the SetRequest-PDU message contains a specification for variables whose values are to be modified by the network administrator. Remember that SNMP does not include specific commands to let a network administrator control a managed device. This is in fact the “control method”, by setting variables that affect the operation of the managed device.
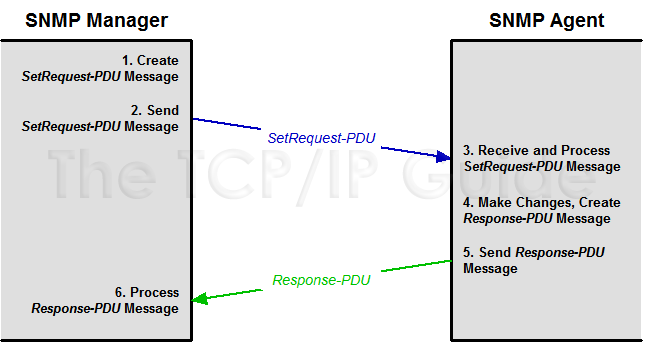
The set process is the complement of the get process; the same basic idea, pretty much, but a reversal in how the object values “travel” and what is done with them. The process follows these steps (see Figure 275):
- SNMP Manager Creates SetRequest-PDU:
Based on the information changes specified by the user through the SNMP
application, the SNMP software on the network management station creates
a SetRequest-PDU message. It contains a set of MIB object names
and the values to which they are to be set.
- SNMP Manager Sends SetRequest-PDU:
The SNMP manager sends the PDU to the device being controlled.
- SNMP Agent Receives and Processes
SetRequest-PDU: The SNMP agent receives and processes the
set request. It examines each object in the request along with the value
to which the object is to be set, and determines if the request should
or should not be honored.
- SNMP Agent Makes Changes and Creates
Response-PDU: Assuming that the information in the request
was correct (and any security provisions have been satisfied), the SNMP
agent makes changes to its internal variables. The agent creates a Response-PDU
to send back to the SNMP Manager, which either indicates that the request
succeeded, or contains error codes to indicate any problems with the
request found during processing.
- SNMP Agent Sends Response-PDU:
The agent sends the response back to the SNMP Manager.
- SNMP Manager Processes Response-PDU:
The manager processes the information in the Response-PDU to see the
results of the set.
Figure 275: SNMP Object Modification Process
The communication process for setting a MIB object value is very similar to that used for reading one. The main difference is that, of course, the object values are sent from the SNMP Manager to the SNMP Agent, carried in the SetRequest-PDU message.
Obviously, telling a device to change a variable's value is a more significant request than just asking the device to read the value. For this reason, the managed device must very carefully analyze and verify the information in the request to ensure that the request is valid. The checks performed include:
- Verifying the names of the objects to be changed.
- Verifying that the objects are allowed to be
modified (based on their Access or Max-Access object
characteristic.)
- Checking the value included in the request to ensure that its type and size are valid for the object to be changed.
This is also a place where general protocol security issues become more important.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: SNMP network management stations control the operation of managed devices by changing MIB objects on those devices. This is done using the SetRequest-PDU message, which specifies the objects to be modified and their values.
Key Concept: SNMP network management stations control the operation of managed devices by changing MIB objects on those devices. This is done using the SetRequest-PDU message, which specifies the objects to be modified and their values.