|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
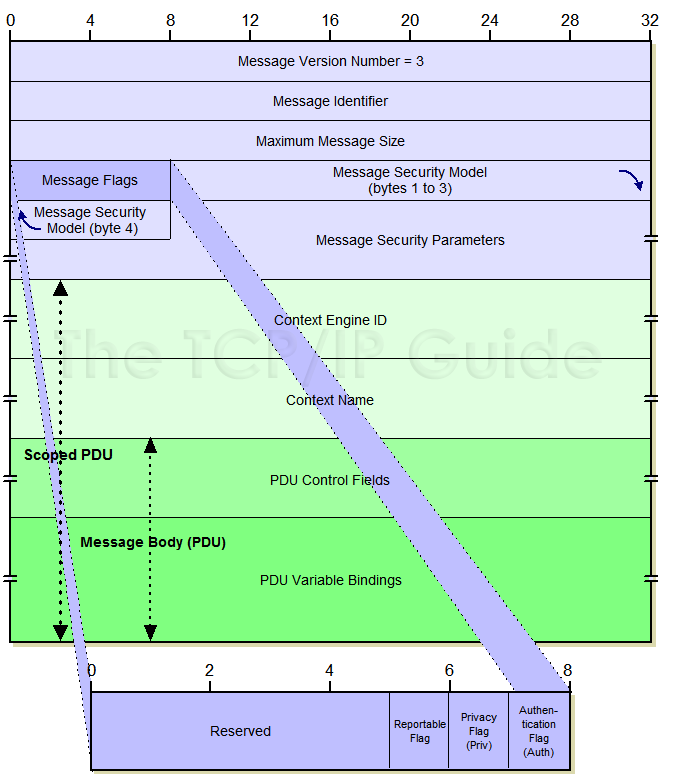
SNMP Version 3 (SNMPv3) Message Format
In the late 1990s, SNMP version 3 was created to resolve the problems that occurred with the many different variations of SNMPv2. The SNMPv3 Framework adopts many components that were created in SNMPv2, including the SNMPv2 protocol operations, PDU types and PDU format. Amongst the significant changes made in SNMPv3 include a more flexible way of defining security methods and parameters, to allow the coexistence of multiple security techniques.
The general message format for SNMPv3 still follows the same idea of an overall message “wrapper” that contains a header and an encapsulated PDU. However, in version 3 this concept is further refined. The fields in the header have themselves been divided into those dealing with security and those that do not deal with security matters. The “non-security” fields are common to all SNMPv3 implementations, while the use of the security fields can be tailored by each SNMPv3 security model, and processed by the module in an SNMP entity that deals with security. This solution provides considerable flexibility while avoiding the problems that plagued SNMPv2.
The overall SNMPv3 message format is described in RFC 3412, which describes version 3 message processing and dispatching. It is shown in Table 221 and Figure 285.
Field Name |
Syntax |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Msg Version |
Integer |
4 |
Message Version Number: Describes the SNMP version number of this message; used for ensuring compatibility between versions. For SNMPv3, this value is 3. |
Msg ID |
Integer |
4 |
Message Identifier: A number used to identify an SNMPv3 message and to match response messages to request messages. The use of this field is similar to that of the Request ID field in the PDU format (see Table 218), but they are not identical. This field was created to allow matching at the message processing level regardless of the contents of the PDU, to protect against certain security attacks. Thus, Msg ID and Request ID are used independently. |
Msg Max Size |
Integer |
4 |
Maximum Message Size: The maximum size of message that the sender of this message can receive. Minimum value of this field is 484. |
Msg Flags |
Octet String |
1 |
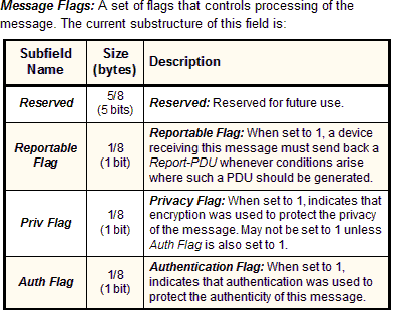
|
Msg Security Model |
Integer |
4 |
Message Security Model: An integer value indicating which security model was used for this message. For the user-based security model (the default in SNMPv3) this value is 3. |
Msg Security Parameters |
— |
Variable |
Message Security Parameters: A set of fields that contain parameters required to implement the particular security model used for this message. The contents of this field are specified in each document describing an SNMPv3 security model. For example, the parameters for the user-based model are in RFC 3414. |
Scoped PDU |
— |
Variable |
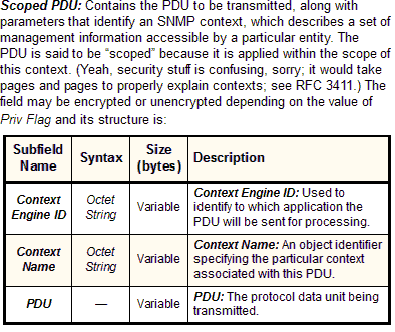
|
And now, let's look at the PDU format for SNMPv3. Ah ha! We are spared this, because SNMPv3 uses the protocol operations from SNMPv2; this is described in RFC 3416, which is just an update of RFC 1904. Thus, the PDU formats are the same as in the previous topic. Phew!
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.