|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
DHCP Options, Option Format and "Option Overloading"
(Page 2 of 4)
Options and Option Format
DHCP maintains, formalizes and further extends the idea of using the Vend field to carry general-purpose parameters. Instead of being called vendor information extensions, or vendor information fields, these fields are now called simply DHCP options. Similarly, the Vend field has been renamed the Options field, reflecting its new role as a way of conveying vendor-independent options between client and server.
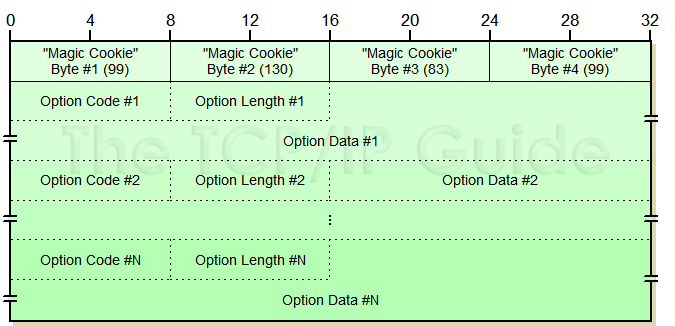
Keeping with the desire to maintain compatibility between BOOTP and DHCP, the DHCP Options field is in most ways the same as the vendor-independent interpretation of the BOOTP Vend field introduced by RFC 1048. The first four bytes of the field still carry the “magic cookie” value “99.130.83.99” to identify the information as vendor-independent option fields. The rest of the Option field consists of one or more subfields, each of which has a “type, length, value” (TLV-encoded) substructure as in BOOTP. The main differences between BOOTP vendor information fields and DHCP options are the field names and the fact that the DHCP Options field is variable in length where the BOOTP Vend field is fixed at 64 bytes. The structure of the DHCP Options field as a whole is shown in Figure 268; the subfield names of each option are described in Table 190.
|
Subfield Name |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Code |
1 |
Option Code: A single octet that specifies the option type. |
Len |
1 |
Option Length: The number of bytes in this particular option. This does not include the two bytes for the Code and Len fields. |
Data |
Variable |
Option Data: The data being sent, which has a length indicated by the Len subfield, and which is interpreted based on the Code subfield. |
All of the DHCP options follow the format of Table 190, except for two special cases, again the same as BOOTP. A Code value of 0 is used as a pad, when subfields need to be aligned on word boundaries; it contains no information. The value 255 is used to mark the end of the vendor information fields. Both of these codes contain no actual data, so to save space, when either is used just the single Code value is included; the Len and Data fields are omitted. A device seeing a Code value of 0 just skips it as filler; a device seeing a Code value of 255 knows it has reached the end of the fields in this Options field.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.