 |
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
ICMPv4 Redirect Messages
(Page 2 of 3)
ICMPv4 Redirect Message Format
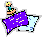
The format for ICMPv4 Redirect messages can be found in Table 92 and Figure 144.
Field Name |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Type |
1 |
Type: Identifies the ICMP message type; for Redirect messages this value is 5. |
Code |
1 |
Code: Identifies the meaning or “scope” of the Redirect message. See Table 93 for an explanation of how this field is used in Redirect messages. |
Checksum |
2 |
Checksum: 16-bit checksum field for the ICMP header, as described in the topic on the ICMP common message format. |
Internet Address |
4 |
Internet Address: The address of the router to which future datagrams sent to the original destination should be sent. |
Original Datagram Portion |
Variable |
Original Datagram Portion: The full IP header and the first 8 bytes of the payload of the datagram that led to the creation of the Redirect. |
When a Redirect is received back by a device, it inspects the included portion of the original datagram. Since this contains the original destination address of the redirected target device, this tells the original sender which addresses should be redirected in the future. The Internet Address field tells it what router it should use for subsequent datagrams. The Code field tells the sender how broadly to interpret the redirection. There are four different Code values; see Table 93.
|
Obviously, routers usually generate Redirect messages and send them to hosts; hosts do not normally create them. The specific rules for when Redirects are created can be fairly complex, as a number of conditions may exist that preclude these messages from being sent. In particular, special rules exist for when a router may Redirect an entire network (or subnet) instead of just a single host. Also, remember that the Type Of Service field is optional and often not used, so Redirects with Code values of 2 or 3 are less common than those with values of 0 and 1.
Code Value |
Message Subtype |
Meaning |
0 |
Redirect Datagrams For The Network (Or Subnet) |
Redirect all future datagrams sent not only to the device whose address caused this Redirect, but also datagrams sent to all other devices on the network (or subnet) where that device is located. (This code is now obsolete; see the note that follows this table.) |
1 |
Redirect Datagrams For The Host |
Redirect all future datagrams only for the address of the specific device to which the original datagram was sent. |
2 |
Redirect Datagrams For The Type Of Service (TOS) and Network (Or Subnet) |
As for Code value 0, but only for future datagrams that have the same Type Of Service (TOS) value as the original datagram. (This code is now obsolete; see the note that follows this table.) |
3 |
Redirect Datagrams For The Type Of Service (TOS) and Host |
As for Code value 1, but only for future datagrams that have the same Type Of Service (TOS) value as the original datagram. |
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Note: One problem with Redirects for whole networks is that the network specification may be ambiguous in an environment where subnetting or classless addressing are used. For this reason, the use of Code values 0 and 2 was prohibited by RFC 1812; they are considered obsolete on the modern Internet.
Note: One problem with Redirects for whole networks is that the network specification may be ambiguous in an environment where subnetting or classless addressing are used. For this reason, the use of Code values 0 and 2 was prohibited by RFC 1812; they are considered obsolete on the modern Internet.