|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
IP Address Size, Address Space and "Dotted Decimal" Notation
(Page 2 of 3)
IP Address "Dotted Decimal" Notation
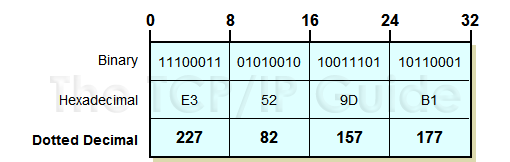
Most people still find hexadecimal a bit difficult to work with. So IP addresses are normally expressed with each octet of 8 bits converted to a decimal number and the octets separated by a period (a “dot”). Thus, the example above would become 227.82.157.177, as shown in Figure 56. This is usually called dotted decimal notation for rather obvious reasons. Each of the octets in an IP address can take on the values from 0 to 255 (not 1 to 256, note!) so the lowest value is theoretically 0.0.0.0 and the highest is 255.255.255.255.
|
Dotted decimal notation provides a convenient way to work with IP addresses when communicating amongst humans. Never forget that to the computers, the IP address is always a 32-bit binary number; the importance of this will come in when we look at how the IP address is logically divided into components in the next topic, as well as when we examine techniques that manipulate IP addresses, such as subnetting.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: IP addresses are 32-bit binary numbers, which can be expressed in binary, hexadecimal or decimal form. Most commonly, they are expressed by dividing the 32 bits into four bytes and converting each to decimal, then separating these numbers with dots to create dotted decimal notation.
Key Concept: IP addresses are 32-bit binary numbers, which can be expressed in binary, hexadecimal or decimal form. Most commonly, they are expressed by dividing the 32 bits into four bytes and converting each to decimal, then separating these numbers with dots to create dotted decimal notation.