|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
IP Subnetting Step #2: The Key Design Trade-off: Partitioning Network Address Host Bits
(Page 2 of 3)
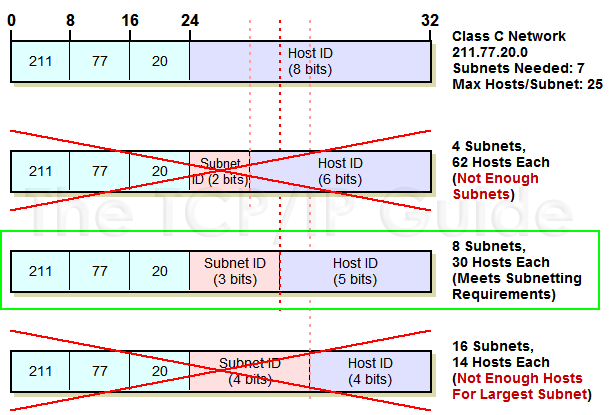
Class C Subnetting Design Example
Let's take an example. Suppose we have a Class C network, base address 211.77.20.0, with a total of 7 subnets. The maximum number of hosts per subnet is 25. Looking at the subnetting summary table for Class C, the answer is instantly clear: we need 3 bits for the subnet ID. Why? This allows us 8 subnets and 30 hosts per subnet. If we try to choose 2 bits, we can't define enough subnets (only 4). As Figure 74 shows, if we choose 4 bits for the subnet ID, then we can only have 14 hosts per subnet.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.