|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
IPv6/IPv4 Address Embedding
(Page 1 of 2)
Due to the importance of the Internet Protocol and the significance of the changes made in IPv6, deployment of the newer version of the protocol will not occur all at once. A transition from IPv4 to IPv6 will be required, which requires careful planning. It is anticipated that the migration from IPv4 to IPv6 will take many years. I discuss this in a special topic dedicated to IPv4/IPv6 transition issues.
IPv6 is backward compatible with IPv4, provided that special techniques are used. For example, to enable communication between "islands" of IPv6 devices connected by IPv4 networks, tunneling may be employed. To support IPv4/IPv6 compatibility, a scheme was developed to allow IPv4 addresses to be embedded within the IPv6 address structure. This method takes regular IPv4 addresses and puts them in a special IPv6 format so they are recognized as being IPv4 addresses by certain IPv6 devices.
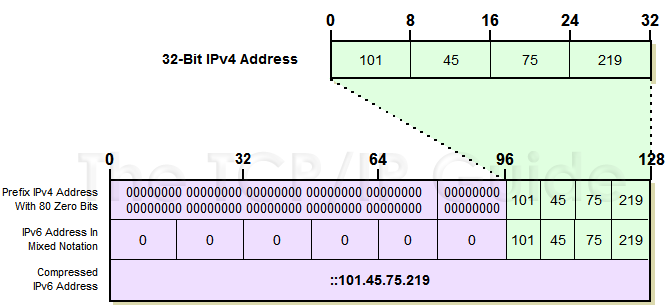
Since the IPv6 address space is so much bigger than that of IPv4, embedding the latter within the former is easy; it's like tucking a compact sedan into the hold of a cargo ship. The embedding address space is part of the reserved address block whose addresses begin with eight zero bits, but only a relatively small part of it. Two different embedding formats are used. Both have zeroes for the first 80 bits of the address, and put the embedded IPv4 address into the last 32 bits of the IPv6 address format. They differ on the value of the 16 remaining bits in between (bits 81 to 96, counting from the left):
The two embedding formats are used in order to indicate the capabilities of the device using the embedded address.
These are special addresses assigned to IPv6-capable devices, such as so-called “dual stack” devices that speak both IPv4 and IPv6. They have all zeroes for the middle 16 bits; thus, they start off with a string of 96 zeroes, followed by the IPv4 address. An example of such an address, shown in Figure 99, would be 0:0:0:0:0:0:101.45.75.219 in mixed notation, or more succinctly, ::101.45.75.219.
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.