|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
IPv6 Datagram Overview and General Structure
(Page 2 of 2)
IPv6 General Datagram Structure
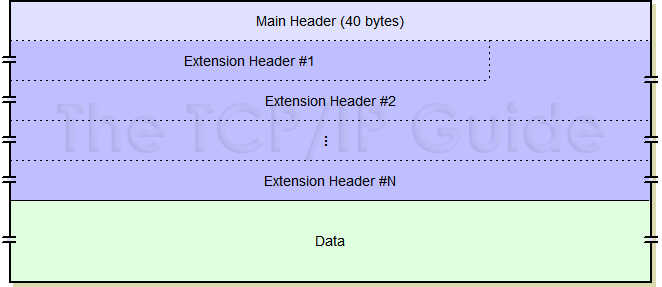
As I mentioned above, IPv6 datagrams now includes a main header format (which has no official name in the standards, it's just “the header”) and zero or more extension headers. The overall structure therefore is as shown in Table 67 and Figure 104.
Component |
Number of Components Per Datagram |
Size (bytes) |
Description |
Main Header |
1 |
40 |
Contains the source and destination addresses, and important information required for every datagram. |
Extension Headers |
0 or more |
Variable |
Each contains one type of extra information to support various features, including fragmentation, source routing, security and options. |
Data |
1 |
Variable |
The payload from the upper layer to be transmitted in the datagram. |
|
Note that as with IPv4, large payloads may be fragmented prior to encapsulation, to ensure that the total size of the datagram doesn't exceed the maximum size permitted on an underlying network. However, the details of fragmentation in IPv6 are different than in IPv4.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.