|
|
Please Whitelist This Site?
I know everyone hates ads. But please understand that I am providing premium content for free that takes hundreds of hours of time to research and write. I don't want to go to a pay-only model like some sites, but when more and more people block ads, I end up working for free. And I have a family to support, just like you. :)
If you like The TCP/IP Guide, please consider the download version. It's priced very economically and you can read all of it in a convenient format without ads.
If you want to use this site for free, I'd be grateful if you could add the site to the whitelist for Adblock. To do so, just open the Adblock menu and select "Disable on tcpipguide.com". Or go to the Tools menu and select "Adblock Plus Preferences...". Then click "Add Filter..." at the bottom, and add this string: "@@||tcpipguide.com^$document". Then just click OK.
Thanks for your understanding!
Sincerely, Charles Kozierok
Author and Publisher, The TCP/IP Guide
|
|
|

Custom Search
|
|
TCP Connection Establishment Process: The "Three-Way Handshake"
(Page 3 of 4)
Normal Connection Establishment: The "Three Way Handshake"
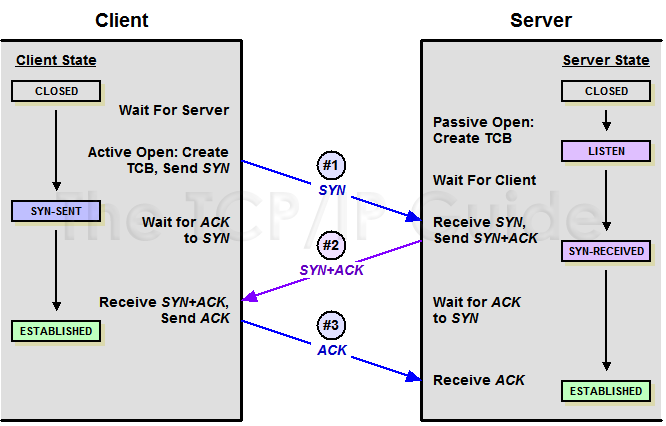
To establish a connection, each device must send a SYN and receive an ACK for it from the other device. Thus, conceptually, we need to have four control messages pass between the devices. However, it's inefficient to send a SYN and an ACK in separate messages when one could communicate both simultaneously. Thus, in the normal sequence of events in connection establishment, one of the SYNs and one of the ACKs is sent together by setting both of the relevant bits (a message sometimes called a SYN+ACK). This makes a total of three messages, and for this reason the connection procedure is called a three-way handshake.
|
Table 152 describes in detail how the three-way handshake works (including a summary of the preparation discussed in the previous topic). It is adapted from the table describing the TCP finite state machine, but shows what happens for both the server and the client over time. Each row shows the state the device begins in, what action it takes in that state and the state to which it transitions. The transmit and receive parts of each of the three steps of the handshake process are shown in the table, as well as in Figure 211.
Client |
Server |
||||
Start State |
Action |
Move To State |
Start State |
Action |
Move To State |
CLOSED |
The client cannot do anything until the server has performed a passive OPEN and is ready to accept a connection. (Well, it can try, but nothing will be accomplished until the server is ready.) |
— |
CLOSED |
The server performs a passive OPEN, creating a transmission control block (TCB) for the connection and readying itself for the receipt of a connection request (SYN) from a client. |
LISTEN |
CLOSED |
Step #1 Transmit: The client performs an active OPEN, creating a transmission control block (TCB) for the connection and sending a SYN message to the server. |
SYN-SENT |
LISTEN |
The server waits for contact from a client. |
— |
SYN-SENT |
The client waits to receive an ACK to the SYN it has sent, as well as the server's SYN. |
— |
LISTEN |
Step #1 Receive, Step #2 Transmit: The server receives the SYN from the client. It sends a single SYN+ACK message back to the client that contains an ACK for the client's SYN, and the server's own SYN. |
SYN-RECEIVED |
SYN-SENT |
Step #2 Receive, Step #3 Transmit: The client receives from the server the SYN+ACK containing the ACK to the client's SYN, and the SYN from the server. It sends the server an ACK for the server's SYN. The client is now done with the connection establishment. |
ESTABLISHED |
SYN-RECEIVED |
The server waits for an ACK to the SYN it sent previously. |
— |
ESTABLISHED |
The client is waiting for the server to finish connection establishment so they can operate normally. |
|
SYN-RECEIVED |
Step #3 Receive: The server receives the ACK to its SYN and is now done with connection establishment. |
ESTABLISHED |
ESTABLISHED |
The client is ready for normal data transfer operations. |
|
ESTABLISHED |
The server is ready for normal data transfer operations. |
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Home - Table Of Contents - Contact Us
The TCP/IP Guide (http://www.TCPIPGuide.com)
Version 3.0 - Version Date: September 20, 2005
© Copyright 2001-2005 Charles M. Kozierok. All Rights Reserved.
Not responsible for any loss resulting from the use of this site.







 Key Concept: The normal process of establishing a connection between a TCP client and server involves three steps: the client sends a SYN message; the server sends a message that combines an ACK for the client’s SYN and contains the server’s SYN; and then the client sends an ACK for the server’s SYN. This is called the TCP three-way handshake.
Key Concept: The normal process of establishing a connection between a TCP client and server involves three steps: the client sends a SYN message; the server sends a message that combines an ACK for the client’s SYN and contains the server’s SYN; and then the client sends an ACK for the server’s SYN. This is called the TCP three-way handshake.